Navigating Eye Flu: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
REVIEWED BY DR. SHOKET ALI (MD MEDICINE) on 09th January 2024.
The eyes, being our most sensitive organ, often suffer neglect in today’s fast-paced world despite constant exposure to screens, digital devices, and environmental pollutants. This negligence can lead to various eye-related issues, including viral conjunctivitis, commonly known as “eye flu.”
Viral and bacterial infections become more prevalent during the rainy season, contributing to the occurrence of eye flu. This condition can be caused by viruses, bacteria, allergens, and environmental factors. In this discussion, we will delve into the symptoms, causes, preventive measures, and treatment options associated with eye flu.
1. What Is Eye Flu?
Eye flu, or viral conjunctivitis, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin layer covering the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid. This condition is primarily caused by viruses, bacteria, allergies, or irritants.
2. How Is Eye Flu Caused?
Viral Origins:
Viruses, such as adenoviruses, are a common culprit behind viral conjunctivitis. These infections can spread through respiratory droplets or by touching surfaces with the virus and then touching the eyes.
Bacterial Causes:
Bacterial conjunctivitis, although less common, can result from bacteria such as Staphylococcus or Streptococcus. It often occurs simultaneously with an upper respiratory infection.
Allergies and Irritants:
Allergic conjunctivitis can be triggered by allergens like pollen or pet dander. Irritants such as smoke and pollutants can also cause eye discomfort.
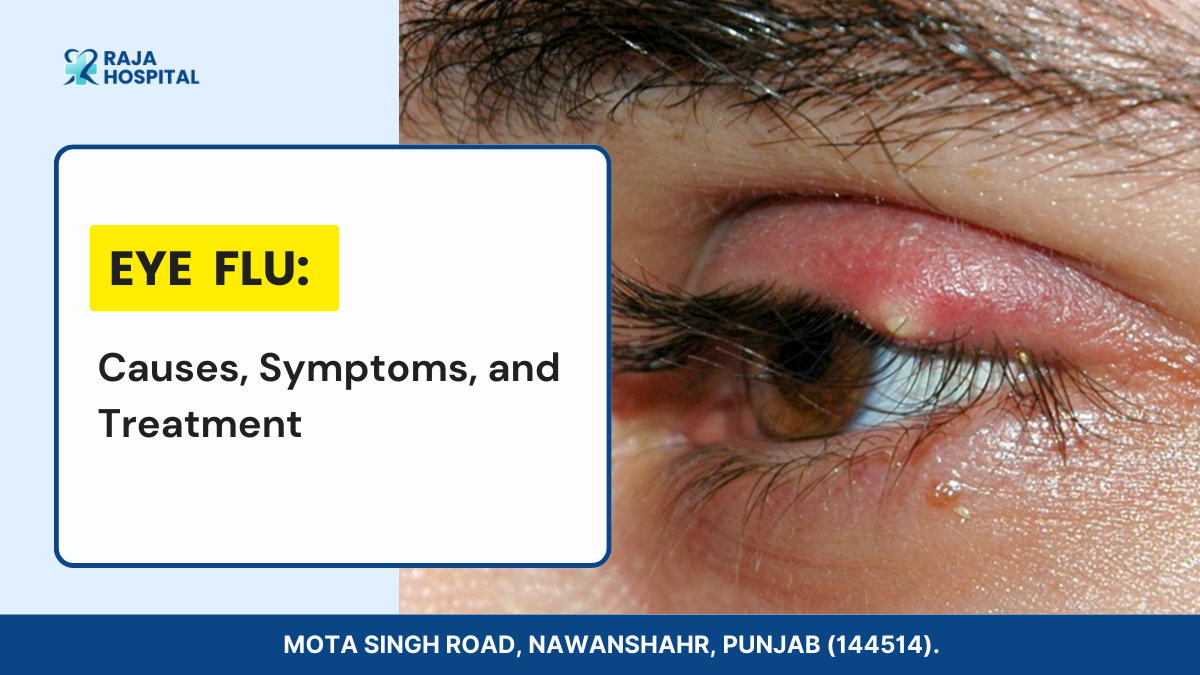
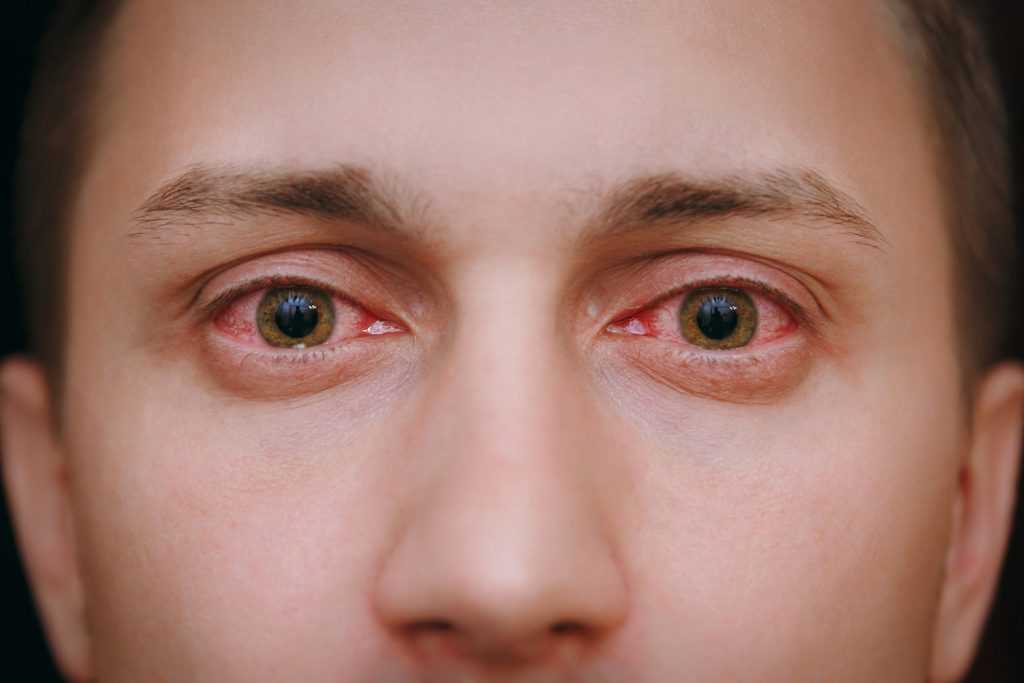
3. What Are Eye Flu Symptoms?
- Redness and Irritation: The primary indicators are redness and irritation caused by inflammation of the eye’s conjunctiva. This leads to visible pinkness as the blood vessels in the eyes dilate.
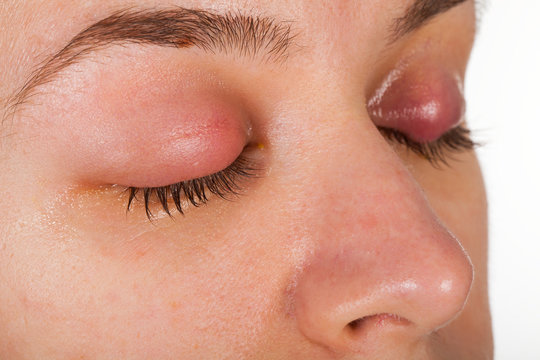
- Swelling of Eyelids: Swelling of the eyelids, primarily due to allergies, is a possible symptom. Allergic conjunctivitis can result in eyelid edema, making the eyes appear puffy and swollen.
- Discomfort While Blinking: Blinking may cause discomfort or pain due to conjunctival inflammation, exacerbating itchiness and discomfort.
- Eye Discharge: The presence of discharge is a notable symptom. Bacterial conjunctivitis often produces a thick, sticky discharge, typically yellow or greenish, causing eyelids to stick together. Viral conjunctivitis may result in a watery or clear discharge.
- Watery Eyes: Excessive tear production, a result of conjunctival inflammation, leads to watery or teary eyes. This can cause discomfort and blurred vision, making daily activities challenging.
- Sensitivity to Light: Eye flu sufferers may experience photophobia, an increased sensitivity to light. Exposure to bright lights or sunlight can induce discomfort and pain, prompting individuals to squint or shield their eyes.
4. What Are Eye Flu Treatment Options?
Home Remedies:
- Apply warm compresses to reduce discomfort.
- Use artificial tears to soothe dryness.
- Avoid touching or rubbing the eyes.
Over-the-Counter Medications:
- Lubricating eye drops can alleviate symptoms.
- Antihistamine eye drops can be beneficial for allergic conjunctivitis.
Prescription Medications:
- In severe cases, prescription eye drops or ointments may be recommended.

Importance of Rest and Eye Care:
- Adequate rest is crucial for a swift recovery.
- Avoid contact lens use until symptoms resolve.
What Are The Prevention Measures To Control Eye Flu Symptoms?
Hygiene Practices:
- Wash hands regularly, especially after touching the face.
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels or cosmetics.
Avoiding Contact:
- Steer clear of individuals with contagious eye infections.
- Refrain from sharing eye drops or makeup.
Environmental Factors:
- Minimize exposure to allergens or irritants.
- Maintain clean indoor air quality.
Timely Treatment of Underlying Conditions:
- Promptly treat respiratory infections to reduce the risk of secondary conjunctivitis.
When To Seek Medical Attention?
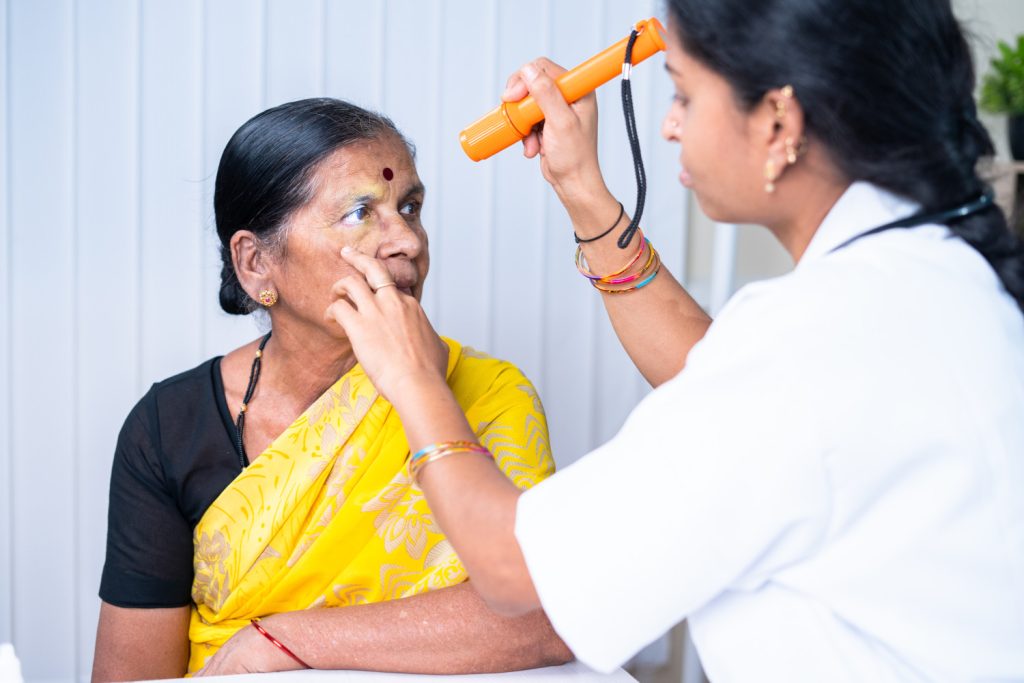
It is important to consult a medical professional if you notice the following conditions:
- Intense Pain
- If you encounter severe eye pain or a sudden decline in vision, seek medical attention promptly.
- Persistent Symptoms
- If your symptoms endure for more than two weeks or worsen, it is advisable to undergo a medical evaluation.
- Suspected Bacterial Infection
- If the discharge from your eyes becomes thick, green, or yellow, indicating a potential bacterial infection, it is essential to consult your doctor regarding the appropriate treatment for eye flu.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of eye flu empowers individuals to take proactive measures for prevention and timely intervention. By adopting proper hygiene, recognizing symptoms early on, and seeking medical attention when necessary, one can effectively manage and overcome eye flu, ensuring a rapid return to optimal eye health.
